What is the Search Engine Optimization (SEO) process and how does it work?
In the vendor – client scenario, a successful search engine optimization process helps to ensure the campaign is set up properly, executed efficiently over time. This chain of events ultimately delivers a positive return on investment (ROI) for the client.
At the beginning, we recommend having the step-by-step SEO process integrated into the client’s proposal – and reviewing the process with them before the project is started.
A strong review allows the customer to understand not only how things will take place, but also see that their involvement (and input) can help the campaign achieve even higher results.
Across the Internet, you will see many processes varying in the # of steps; usually between 5-10. The main thing to understand is there are numbered steps that need to be followed… and not a “fly by the seat of your pants” approach to doing SEO. The aforementioned always ends badly for both parties and can be easily avoided.
“A team using process methodology achieves more gain than the sum total of individual effort.“
There are Two Major Parts of SEO
Follow A Step-by-Step Process- We Do!
- Step 1: Keyword Analysis
- Step 2: Website Audit
- Step 3: Landing Page Optimization
- Step 4: Blog Integration
- Step 5: Meta Elements
- Step 6: Citation Building
- Step 7: Blog Posting
- Step 8: Link Building
- Step 9: Google Business Profile Optimization
- Step 10: Reporting
Step 1: Keyword Analysis (Setup: On-Page)
Keyword selection is a crucial step in our SEO process, requiring close collaboration between our team and the client. This phase often involves multiple iterations, as we refine the keyword list by removing irrelevant terms and adding new ones to better align with the client’s objectives.
It’s important to note that PalmettoSoft typically conducts keyword analysis during the sales process, even before starting the SEO process outlined here. This early keyword analysis helps us gain a deeper understanding of the client’s business, which is essential for tailoring our SEO strategy.
For clarity and ease of presentation, however, we are showcasing this as the first step in our SEO process.
How We Conduct Keyword Analysis
We begin by having an initial sales conversation to learn about the client’s business and marketing goals. After this discussion, we ask the client to provide a list of keywords they believe potential customers might use to find their services or products.
Using this initial list, we employ our free research tool along with Google Search Console to uncover a more comprehensive set of keywords. We analyze factors like monthly search volume and competition levels to refine this list. Once completed, we send the refined list to the client for review.
To ensure the client fully understands the data, we follow up with a phone call. During this call, we explain any technical terms and offer guidance on selecting the most effective keywords.

The Google Keyword Planner is a great free tool
Image source: Google Keyword Planner
Key Considerations in Keyword Analysis
Relevance: Our primary focus is on relevance. Long-tail keywords, which often consist of four or five words, tend to be more specific and lead to higher conversion rates. These keywords indicate that the searcher knows precisely what they’re looking for, unlike generic terms that may attract irrelevant traffic.
A keyword analysis is very important and requires some back and forth collaboration with the client. You should let them know upfront that you need their input and it’s considered normal to create several versions of the report until the best keywords are discovered.
Competition: This factor is categorized as high, medium, or low. It indicates the number of search results that appear when a keyword is entered into a search engine. High competition means it will generally take more time to achieve a first-page Google ranking. Low competition keywords, on the other hand, typically reach the first page faster.
Monthly Search Volume: This is considered a secondary factor. While it is essential, it takes a backseat to relevance and competition. A high search volume can be attractive, but it’s less beneficial if the keyword isn’t relevant or has too much competition.
Strategic Approach
Focusing on long-tail keywords initially allows for faster ranking on the first page of search results, which can lead to quicker sales. As the client’s business begins to grow through these quick wins, we can gradually expand the keyword list to include more competitive terms, building on early successes to achieve long-term growth.

When selecting keywords, customers often gravitate towards those with the highest monthly search volume. These keywords tend to be broad and generic. For example, if your client specializes in faux alligator handbags, targeting the term “handbags” might not be the best strategy.
Here’s why: Even after investing significant time and money—say, four years and $48,000—you might finally achieve a first-page ranking. However, about 99% of the searchers who click through to the website are unlikely to make a purchase.
Worse still, this generic traffic can lead to a flood of unqualified sales inquiries and a deluge of spam emails. The website might also suffer from a high engagement rate, which occurs when visitors leave the site almost immediately after arriving. A high engagement rate negatively impacts SEO rankings, creating a vicious cycle that’s both a waste of time and money.
The takeaway? Avoid generic, high-competition keywords. They’re often not worth the investment and can do more harm than good in the long run.
Step 2: Website Audit (Setup: On-Page)
Think of a website audit as a health check for your website. The primary goal is to identify any significant technical or functional issues that could impact your site’s performance during the SEO setup process. If any problems are found, they need to be fixed immediately to prevent systemic ranking issues.
In this overview, we will only cover the main elements of a website audit without delving into extensive details. If you’re interested in learning more about each element, plenty of resources are available online. Doing your own research can often help you better understand and retain the information.
It’s crucial to complete all website fixes before starting any off-site SEO work. Just like you wouldn’t land a new jumbo jet on a dirt road, Google’s engineers expect a well-optimized website foundation before ranking your site.
All website fixes should be 100% completed before any off site SEO work is done. Would you land a new jumbo jet on a dirt road? Of course not, and the engineers at Google hold the same view.
Main Elements of a Website Audit
- Technical SEO: Ensuring that the website's technical aspects are optimized for search engines.
- Website Structure: Checking the site's architecture for easy navigation and indexing.
- On-Page SEO: Optimizing individual pages to improve search visibility.
- Website Content Review: Evaluating the quality and relevance of the site’s content.
- Competitors Website Analysis: Understanding what competitors are doing to rank well.
- Design and UX Analysis: Assessing the design and user experience to ensure a seamless and engaging interface.

SEMrush is one of the best website audit tools.
Image source: SEMrush
Much like regular oil changes extend the life and performance of a car, periodic website audits enhance the longevity and effectiveness of your SEO campaign. We recommend conducting a website audit at least once a year.
When to Conduct a Website Audit
Algorithm changes
Regular audits help ensure your site stays optimized and compliant with ever-evolving Google and Yahoo/Bing algorithms.
Webmaster guidelines
Running periodic audits ensures compliance with the major search engines’ Webmaster Guidelines, which is crucial for maintaining rankings.

Skipping or rushing through the website audit can severely impact your ability to rank. Trust the experts: If your meta coding is out of spec or your page loading times are slow, it’s like pouring water into a bucket with a small hole. You might see a temporary rise in performance, but it will eventually lead to a slow, inevitable decline.
No matter how many advanced SEO techniques you implement, if the foundation of your website is flawed, your SEO strategy will be as unstable as a house of cards.
Step 3: Landing Page Optimization (Setup: On-Page)
Once keyword selection and the website audit are complete, the next critical step is landing page optimization.
In most cases, websites will require the creation of a few new pages to support the newly selected keywords. While it’s rare, some existing pages can occasionally be optimized for these new keywords. For example, if a client selects 10 keywords for their campaign, it’s common to plan for the creation of three to four new landing pages within the main site navigation.
Years ago, search engines required each keyword to have its own landing page, which often resulted in websites with excessive keyword repetition and clutter.
Thankfully, search engines today are more advanced, allowing several related keywords to be targeted on a single page in a more natural and streamlined structure.
Landing pages support the targeted keywords for your campaign. However, don’t just have a page full of copy… add supporting images, call to action buttons and make the page “come to life.” You will have higher conversion when you do this.

Landing pages typically follow a template style for consistency & conversion.
Image source: Unbounce
Important Elements of a Successful Landing Page
- Clear value proposition
- Engaging banner image with strategic messaging
- Benefits of the product or service clearly stated
- Customer testimonials to build credibility
- Call-to-action buttons to encourage engagement
- Quick contact form for ease of communication
Where to Install Landing Pages
1. In the Footer
A common approach is to add keyword-targeted landing pages to the website’s footer or sitemap, which keeps the top navigation clean and uncluttered. This placement ensures that search engines view these pages as part of the site’s “first-level navigation,” giving them the appropriate authority when indexing.
When users search on Google, they will land directly on the optimized page through the search result link. Additionally, the footer placement allows users to be just one click away from the main sections of the site, such as the home page.
2. In the Main Navigation
Another option is to integrate landing pages into the main navigation of the website. While this can be more challenging, it provides an opportunity to make the navigation look more cohesive and naturally aligned with the targeted keywords.
When done successfully, this approach can result in higher customer conversion rates because the site feels more intuitively structured around the keyword focus areas.

Be cautious when dealing with clients who are overly attached to the design of their website. This is especially common when the client has designed the site themselves and feels emotionally invested in its appearance. When you recommend adding landing pages or making changes for SEO purposes, you might encounter resistance or suggestions for awkward workarounds. Avoid implementing these suggestions, as they often compromise the necessary SEO work.
For instance, we’ve heard comments like, “I don’t want keywords on my homepage. I wrote the copy myself, and I think it looks great.” While the design may look good, it’s important to remind clients that effective SEO requires balancing aesthetics with functionality to achieve the best results.
Step 4: Blog Integration (Setup: On-Page)
Over the past several years, blogging has become a critical component of an effective SEO strategy. It’s a powerful way to drive traffic, build trust, and consistently add fresh content to your site, which search engines value.
Once we’ve installed WordPress, our preferred development platform, integrating a blog is the next step. This includes setting up both an overview and detail page for maximum SEO benefit. The overview page presents a list of blog posts, while the detail page allows for more in-depth individual posts.

WordPress offers a robust blog with a lot of plugins.
Image source: WordPress
WordPress Plugins We Use
To enhance SEO and functionality, we integrate the following WordPress plugins:
- Breadcrumb NavXT: Adds breadcrumb navigation to improve user experience and site structure.
- Social Warfare: Encourages social sharing to increase reach and engagement.
- 301 Redirection: Manages URL redirects to preserve SEO rankings when pages are moved or deleted.
- Yoast SEO: Optimizes on-page SEO for better search engine rankings.
- wpDiscuz: Adds interactive commenting features to promote engagement.
- Broken Link Checker: Identifies and fixes broken links to maintain site health.
- Rel NoFollow Checkbox: Allows the option to add "nofollow" tags to outbound links.
- All in One Schema Rich Snippets: Implements schema markup for better SERP visibility.
Blog Navigation and Visibility
It’s essential to create a top navigation link and a footer link for your blog. This signals to both visitors and search engines that your blog is a vital part of your website. By making your blog more visible, you’ll increase readership and show Google that you’re consistently producing new, valuable content, rather than running a static website.
Your website blog can be one of the biggest SEO drivers on your website. Set it up correctly, with all the appropriate functionality- and write content with teeth! Your visitors will appreciate it and the search engines will reward you handsomely. Never underestimate the power of your blog!

Never approach blogging with the mindset that it’s just a task you need to check off your list. If you do, you risk becoming part of the sea of mediocre bloggers who waste time and effort with uninspired content.
Instead, write about topics you’re passionate about or knowledgeable in. Both your readers and search engines appreciate engaging, informative content, so always put in your best effort. This mindset will benefit all areas of copywriting on your website.
Additionally, don’t shy away from having a strong opinion. While you should avoid profanity, disrespectful language, or over-the-top claims that could alienate or offend your audience, being too vanilla can make your content forgettable. Strive for authenticity and balance.
Remember this: If you’ve made it this far into reading, it means the content held your attention—proof that engaging content works!
Step 5: Meta Elements (Setup: On-page)
Meta elements, also referred to as metadata or meta coding, are one of the fundamental components of any SEO strategy. Although they’ve been around for a long time, they remain just as important today.
In essence, meta elements are hidden pieces of information in your website’s code that inform search engines about the content and purpose of your site. They don’t appear to the public but play a crucial role in how search engines understand and rank your pages.
Why Meta Elements Matter
It’s essential to ensure that your meta elements are optimized and aligned with search engine parameters. In simple terms, meta elements tell search engines what each page on your website is about. For best results, the actual page content should be consistent with your meta elements. Search engines like Google compare both, and this consistency is a key factor in their ranking algorithm.
Make sure you do your meta coding correctly and to the search engine’s parameters. After all, you are talking directly to the search engines about your website’s content.
Key Meta Elements to Optimize
To ensure your website is properly optimized, focus on the following meta elements:
- Title Tag: The main title that appears in search engine results.
- Meta Description: A brief summary of the page's content that also appears in search results.
- Meta Keywords: Although less relevant now, some search engines may still consider them.
- Heading Tags (H1, H2, etc.): Help structure your content and guide search engines.
- Image Alt Text: Describes images for both accessibility and SEO purposes.
- Breadcrumb Navigation: Aids both user experience and search engines in understanding your site's structure.
- Schema Markup: Adds structured data to help search engines understand your content better.
- Sitemap.xml Setup: Guides search engines through your site, improving crawl efficiency.
- Robots.txt Setup: Instructs search engines on which pages to crawl and index.
- Custom 404 Error Pages: Enhances user experience when visitors encounter broken links.
- 301 Redirect Verification: Ensures that old or deleted pages properly redirect to preserve SEO value.
- Internal Content Linking: Helps search engines understand the relationship between pages.
- Google Webmaster Tools & Analytics Setup: Tracks SEO performance and monitors for potential issues.

Meta Coding is what the search engines sees, and not your visitors.
Image source: deepfieldinc.com

Avoid SEO Shortcuts
Over the years, many have tried to manipulate search engine rankings by stuffing keywords into meta elements or using tactics like “hidden text.” These methods don’t work and can lead to penalties from search engines. In severe cases, this could result in the need for a Reconsideration Request to restore your site’s ranking.
Rest assured, any sneaky ideas you might have about meta elements have likely already been tried, and search engines have addressed them with algorithm updates.
Meta Elements as Your Foundation
Think of optimizing your meta elements like laying the concrete foundation for a house. It’s not flashy, but it’s necessary for the long-term stability of your SEO strategy. With a solid foundation, your SEO efforts will stand on much firmer ground, setting you up for success as you move forward.
Step 6: Citation Building (Setup: Off-Page)
Citation building is a crucial component of local SEO, helping search engines confirm the legitimacy of your business. When your business’s Name, Address, Phone number (NAP), website, and business description are consistently listed across multiple credible websites, it enhances your website’s authority, builds trust, and significantly improves your ability to rank in local search results.
Why Citation Building Matters
Developing a strong citation profile is one of the most fundamental and cost-effective methods for optimizing local SEO. These citations signal to search engines that your business is trustworthy and consistent across the web, making it easier for potential customers to find you.
Developing a strong citation profile for your business is one of the most fundamental and cost-effective methods to optimize for Local SEO.
Key Findings on Citation Building
- 76% of SEOs use citations/directory listings to build links.
- 58% of SEOs use content marketing to build links.
- 24% of SEOs use press releases to build links.
- 21% of SEOs use guest posts to build links.
Source: BrightLocal
Top 10 Free Citation Sites

Consistency is Key
Incorrect or inconsistent NAP information across citation listings can negatively impact your SEO rankings. In severe cases, fixing these inconsistencies can take a lot of time, effort, and money. Worse still, there’s a possibility that your rankings may not fully recover if the errors are significant.
To avoid these issues, always follow best practices and use a reliable citation listing tool to ensure accuracy and consistency across all listings.
Step 7: Blog Posting (Routine: On-Page)
Blog posting plays a vital role in SEO for several reasons:
- It signals to search engines that your site is regularly producing fresh content, leading to more frequent indexing.
- It positions your company as a subject matter expert (SME) in your industry.
- It can drive high-quality inbound traffic to your site, significantly boosting your overall SEO efforts.

The WordPress dashboard is easy to use and allows for robust blog management.
Image source: WordPress
Blog Writing Tips
- Choose blog topics based on keyword research: Ensure the topics you write about are relevant and backed by keyword data.
- Craft a compelling blog post title: Your title should grab attention and include primary keywords.
- Outline your blog with SEO in mind: Structure your content to align with SEO best practices.
- Use keywords strategically: Incorporate keywords naturally throughout the post.
- Cover the topic comprehensively: Ensure your blog fully addresses the subject matter.
- Add SEO-optimized images and videos: Visual content enhances engagement.
- Include image alt text: Optimize images for SEO and accessibility.
- Link to related blog posts: Internal linking strengthens your site structure and SEO.
- Optimize the meta description: Write an enticing and keyword-rich meta description.
- Review metrics regularly: Track blog performance using analytics tools.
Google Analytics and Blog Performance
With Google Analytics 4 installed on your site, you can track essential metrics like page stay times, engagement rate, and visitors per page. This data is not only crucial for evaluating your performance but is also reported back to Google.
In fact, website performance data has become an increasingly important factor in Google’s ranking algorithm. A well-written, SME-focused blog post can drive more traffic than your homepage, which Google favors. When individual pages outperform your homepage, it leads to more stable and higher SEO rankings.
For more on this, check out Google’s Hummingbird update. It enhances the search engine’s ability to direct users to the most relevant page on a site rather than just the homepage.
Strategic Approach
Activate a social sharing widget at the top of your blog to display comments, views, and shares. High engagement numbers tend to attract more readers, which increases visitor stay times—something that Google Analytics tracks and rewards by boosting your post’s rankings.
If you have the talent and passion, write more than 700 words and develop more informative articles. The search engines will reward you for this effort as you are making your website more of a knowledge base instead of an online brochure.
Example

The Google Keyword Planner is a great free tool
Image source: Google Keyword Planner

Avoid using Facebook comments on your blog. Since Facebook is a direct competitor of Google, its comments are not indexed, meaning you miss out on a critical SEO opportunity.
Instead, use Disqus or native WordPress comments, both of which are indexable by search engines. These tools encourage back-and-forth conversations, showing Google that your blog is relevant and generating engagement—both of which help improve your SEO rankings.
Step 8: Link Building (Routine: Off-Page)
In the late ‘90s, when Google first rose to prominence, it began using the number of links pointing to a webpage as a key factor in determining its quality. Initially, the more links a page had, the better. However, as Google evolved, the relevance of those links became more important than the sheer number. Google realized that websites naturally link to other relevant sites, forming a network of related content.
Link building is the process of acquiring high-quality backlinks from other websites to your own. A backlink, typically using keyword-rich anchor text, acts as a bridge for both humans and search engines to navigate between pages across different websites. Link building is one of the most effective and popular off-page SEO techniques, playing a crucial role in Google’s ranking algorithm.d Page Authority (PA), especially those in your niche or related industries.
To boost your rankings, aim to generate quality “do follow” backlinks from websites with high Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA), especially those in your niche or related industries.
Link building is an incredibly important step in SEO. It should be done carefully, routinely and never forced. Always try to think like the search engine when you build links so your strategy has a natural structure to it.
Linking is an extremely important part of SEO and should be done by professionals.
Image source: singlegrain.com
Types of Link Building
Manual Link Building – GOOD
For most SEO campaigns, link building is a manual task. It involves submitting quality, relevant content—such as guest posts, articles, and press releases—to niche websites in order to acquire backlinks. While this process can be time-consuming, the payoff is worth it, as it leads to higher search rankings.
Natural Link Building – EXCELLENT
You’ve probably heard the phrase, “Content is King.” This is especially true in link building. Great content naturally generates backlinks without much effort. Our owner, Rhett DeMille, likes to say, “Content is King, and linking is the Queen.”
Think about a well-researched PDF, a great video, an informative blog post, or a valuable web page—people will want to link to them as references. When this happens, you build a network of high-quality backlinks. In this very post, we’ve linked to related websites to add credibility to what we’re saying. This interlinking of valuable content is the best form of link building.

Using black hat link-building techniques can severely damage your site. You risk being penalized, removed from search results, or even having your domain blacklisted.
For example, if someone suggests that you need to rapidly acquire backlinks to boost your rankings quickly, they might advise purchasing mass backlinks from untrusted or unrelated websites. These low DA sites often create toxic links, which can harm your site’s SEO.
To combat these practices, Google introduced several algorithm updates, including Penguin, which targets websites with spammy or manipulative content.
Our Advice: Always Go White Hat
To ensure long-term success, always follow white hat SEO practices. Do things the right way, focusing on quality rather than shortcuts.
Step 9: Google Business Profile Optimization (Routine: Off-Page)
Google Business Profile (GBP) is a free tool for businesses to manage their online presence across Google, including Search and Maps. It provides an excellent platform for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to display their address, phone number, and other details in Google Maps results. We strongly recommend that all businesses create a GBP listing.
What Makes GBP Unique?
While GBP may resemble a citation listing, it’s much more. Think of it as a business directory and social media profile combined. Citation listings can positively impact GBP rankings, but the two are separate entities that complement each other in a successful local SEO strategy.
Does GBP Require a Website?
A website is not required to create a GBP listing, but having one is highly recommended. Your website serves as the foundation of both on-page and off-page SEO efforts, which, when combined with GBP, create a powerful local SEO strategy.
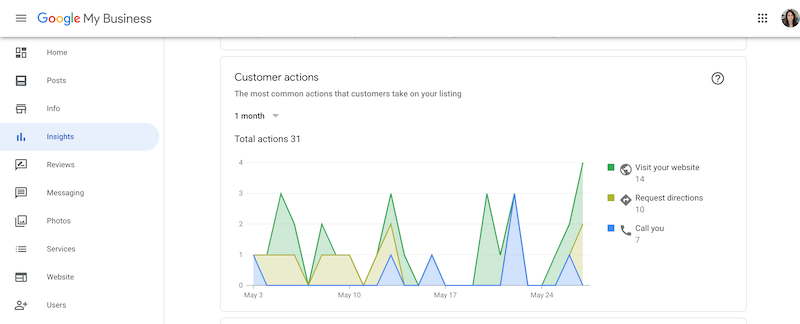
Understanding GBP Insights
Unlike Google Analytics (GA), which is installed on your website, GBP Insights provides performance data for your business listing. It tracks metrics like keyword searches, website visits, calls, and other user interactions, helping you measure the success of your profile.
Google Business Profile is the Internet’s ultimate version of a citation listing and social profile. Put a lot of effort into this and your Local SEO should benefit. Remember this: Nobody loves Google more than… Google (think indexing!).
Google Business Profile Insights shows customer actions within your GBP listing.
Image source: Google Business Profile Insights
Google Business Profile Verification Process
To create and verify a Google Business Profile, follow these steps:
- Go to Google Business and sign up.
- Set up a new Google account (Gmail or G Suite required).
- Enter your business name and address.
- Specify service areas if you’re a Service Area Business.
- Choose your business category.
- Add a contact phone number and website URL.
- Request a verification PIN postcard via mail.
- Once the PIN is received, log in to your GBP profile and click Verify.
- Enter the PIN and complete the verification process.
Google Business Profile Optimization Techniques
Once your GBP is set up, it’s time to optimize it using the following techniques:
- Add Photos and Videos: Regularly upload authentic images and videos. Enable the "Locations" setting on your smartphone for verification.
- Write a Compelling Business Description: Clearly explain what your business offers and optimize it with relevant keywords.
- Use Q&A to Understand Your Audience: Respond to frequently asked questions to better engage with potential customers.
- Create Posts: Showcase offers, promotions, and updates through regular GBP posts.
- Add Service Menus and Product Collections: Highlight your services or products with detailed menus and collections.
- Request and Manage Reviews: Start asking satisfied customers for Google reviews and actively manage them.
- Maintain Your Business Profile: Keep your profile updated to ensure accuracy and relevancy.

Managing Customer Reviews
Positive customer reviews are essential for GBP optimization. The more favorable reviews you receive, the better your business’s reputation, credibility, and branding.
However, negative reviews can occasionally happen. Whether it’s due to a mistake or an unhappy customer, it’s important to handle these reviews professionally. Here are some best practices for addressing negative reviews:
- Assess and evaluate the feedback internally before responding.
- Publicly respond to the review with a calm, professional tone.
- Acknowledge any mistakes and be transparent about what went wrong.
- Ask questions if the details of the complaint are unclear.
- Show empathy and offer solutions to address the issue.
- Sign your name to add a personal touch.
- Request an update to the review once the issue has been resolved.
Source: HubSpot
Following these steps can often turn a negative situation into a positive outcome. In many cases, potential customers will appreciate how you handle feedback, which can improve their perception of your business. Sometimes, the reviewer may even remove or update the negative review after you’ve addressed their concerns.
Step 10: Reporting (Routine: On/Off-Page)
The final step of your SEO process is reporting. This is where both you and the client review the campaign’s performance using clear, consistent metrics. A good report ensures that both parties are on the same page.
Key Elements of an SEO Report
Monthly Campaign Performance Report
Whether you present the report in PDF format, through software, or via a spreadsheet, it should cover essential data such as:
- Keyword rankings
- Website traffic
- Engagement rate
- Page stay times
- Other relevant metrics from Google Analytics
At a minimum, your report should include a summary, technical details, and ROI tracking.
Monthly Client Call
Beyond the written report, it’s important to schedule a monthly call with the client. During the call, review key aspects of the campaign, address questions, and take notes. Recording the call can also help your technical team better understand their responsibilities.
Image source: Google Image
Elements of a Monthly Campaign Performance Report
Market Analysis – Trends We Are Seeing
Start by discussing high-level insights in simple terms. Share something noteworthy that the client will find interesting, backed up by data.
For example, you might say:
“From May to July 2020, searches for ‘disinfection services’ increased by 9,328.57%. We recommend adding at least five new keywords related to disinfection to your campaign.”
Performance – How the Campaign is Progressing
Here, you present the technical details such as keyword rankings, website traffic, engagement rate, page speed, and more. While this data is valuable to SEO experts, it may not mean much to your client.
Tip: Don’t make this section the main focus of your report. Instead, interpret the data in terms of how it benefits the client’s business.
Recommendations
Based on the data, provide proactive recommendations. These could include refreshing website content, adding new plugins, or creating a new page that explains a key business process.
Adjustments
Highlight recent changes or updates made to the campaign. For example, maybe you added an anniversary banner to the website, optimized meta elements, or worked on a keyword that now ranks on the first page of Google.
ROI Tracking
If your client is ready for advanced tracking, setting up ROI tracking can be incredibly valuable. It helps justify the campaign by showing a direct return on investment.
A simple ROI formula:
ROI = (Net return / Cost of investment) × 100%
For example:
If the client made a $15,000 profit and your SEO services cost $3,000, the ROI is:
$15,000 / $3,000 × 100 = 500%
You can set up ROI tracking for E-commerce as well with some basic adjustments.
Professional level reporting is like hitting the top of the striker bell at the fair. This is where both the client and vendor can see success.
Reporting is the most important step of the SEO Process. Numbers don’t lie and when you are really good at what you do, it shows. Always strive to improve your reporting process and everything else you do in SEO will improve as a result!
Final Thoughts on Reporting
Reporting is a critical part of the SEO process. A well-structured report builds client confidence and increases the likelihood of client retention, upselling services, and gaining referrals.
If you’re new to reporting, keep it simple, clear, and to the point. Over time, you can expand your reports by adding valuable sections that align with your growing expertise. For seasoned professionals, detailed reports showcase your skills and help clients see the tangible benefits of your efforts.

Manage Client Expectations
During the reporting process, always stick to the terms outlined in your contract. Be cautious about agreeing to any additional tasks the client may request during the review or monthly call.
For example, if your contract states, “gain first-page rankings for each keyword within a specific time frame,” that means any position on the first page qualifies as meeting the goal. If the client suddenly asks for a #1 ranking for a keyword (especially if Wikipedia holds the top spot), agreeing to this request could result in a long-term, uncompensated effort.
Tip: Review the proposal with the client before starting their SEO campaign. If the client requests additional work not covered in the contract, kindly explain the scope of your current obligations and offer to provide an updated proposal with revised terms and fees.
Summary
If you are a developer or casual reader, we hope you gained something of value from this article.
While there are many ways to do SEO, this is the way we do it at PalmettoSoft, and we have been quite successful at it. When in doubt about a technique, you should always do your research to find the best white hat method.
And if you are still stumped, feel free to contact us and we will do our best to steer you in the right direction.
Don’t forget that a website needs one complete content refreshment per year at minimum. Otherwise, your rankings will start to get stale.
Finally, your best performing campaigns tend to be the ones where your customers take a personal interest in SEO for their business. After all, their input and thoughts can help provide critical guidance to long-term success.
Now let’s transition into the technical stuff.
FAQs
SEO, or search engine optimization, is the continual process of improving a website’s ranking in the organic search results. Work is done both on the website and off the site (technically known as On-page SEO and Off-page SEO) in the effort to target keywords which match what the business/organization wants to be found online for. Ultimately, these keywords should be boosted to the 1st page of the SERPs (search engine results pages).
“For example, for a typical search query, the number one result will receive 40-60% of the total traffic for that query, with the number two and three results receiving significantly less traffic. Only 2-3% of searchers click beyond the first page of search results.”
Source: Optimizely
Once started, SEO work should never stop primarily due to: Continual search engine algorithm updates and competitor movements.
A hypothetical SEO campaign in action: A business manufactures faux alligator purses for sale to the public. It has optimized for many keywords, but a specific few are “fake alligator pocketbook” and “imitation crocodile purses.” When the visitor searches for one of these terms, the business is found on the 1st page search results.
Then, the visitor clicks on the link and visits the website- and ultimately buys a bag. The main goal of the SEO campaign is to deliver as many potential customers as possible to buy these products.
It is also very important to understand that professional SEO is one of the highest ROI marketing activities that a business can do. Why? First, the website owner is not paying for clicks, such as an advertising solution like Google Ads… and secondly: Optimization itself, and the act of doing it, makes the website continually better as a destination for the visitor. Better website = Better conversion.
Takeaway: It can be a great long term online marketing solution.
There are two main areas of SEO:
On-Page: This is work done on the website, such as a meta coding, content interlinking, image ALT Tag, etc…
Off-Page: This is work done off the website, such as promotion which ultimately builds value backlinks.
Many SEO firms, for example, measure campaign size by the number of targeted keywords. For a small campaign, this number in many instances is around (10)
Larger campaigns can sometimes target more than (50), with each keyword “being its own unique battle in order to gain a 1st page search engine results page (SERPs) ranking.”
No, it does not.
PageRank is a ranking algorithm developed in 1998, in which it basically measures the “value” of inbound links to a website. Typically, more links meant an ultimately higher search result ranking.
After years of evolution as well as millions of black hat attempts to cheat PageRank for artificially high results, Google stopped offering the PageRank toolbar to the public in 2013. Nowadays, PageRank is used nominally by Google when ranking websites, and carries exponentially less authority than when it was first created.
The Google algorithm is a machine learning system which attempts to match the most relevant websites to a query in which the user enters into the Google search engine. It is commonly thought in the SEO industry that Google measures hundreds if not thousands of signals within their algorithm.
No… but hold on.
Domain Authority is not a Google ranking factor and has no effect on the SERPs. Domain Authority and Page Authority are ranking formulas developed by Moz.com– a commonly understood search engine authority.
However, in an indirect method, a higher domain authority can help a website rank higher in the search results.
While this is not an exact number, in 2018 for example, Google updated more than 3,000 times. However, these tend to be minor updates with 1-2 major updates occurring each year.
Basically, it updates continually and SEO should never be a one time exercise.
Typically between 4 days to 4 weeks- or more.
Absolutely. In addition, website analytics data is an ever increasing performance metric used in how a website ranks in the SERPs.
Yes, but this was not always the case up until recently. A more informative answer can be found in this article.